Clothing & Textiles /simplified notes for WASSCE
Clothing & Textiles /simplified notes for WASSCE. A precise and concise note on clothing and Textiles
♦Fibres
They are materials used to produce fabrics or a fibre is a flexible tiny hair-like structure used to produce yarns for fabrics.
Types of fibres
_artificial/man-made fibres
-natural fibres
Artificial fibres: They are fibres obtained from man
Types of man- made/artificial fibres-_synthetic fibres-
they are fibres that are purely produced from chemicals eg. Nylon, polyester etc.-
– regenerated fibres- they are fibres produced from the combination of natural materials and chemicals
Natural fibres- They are fibres obtained from natural sources
types of natural fibres
-plant/cellulosic fibres- fibres obtained from plants
-animal fibres/protein fibres- they are fibres obtained from animals
-mineral fibres- they are fibres obtained from rocks
Sources and classification of fibres: – principal origin i.e. Natural and man-made
– chemical type i.e. Cellulosic, protein, mineral, synthetic, (petroleum) regenerated,
– family name or type i.e. Seed, hair, stem, leaf, root, husk, animal skin, animal hair, animal secretion, rock, metallic, plant pulp, petroleum product, by products of natural fibres and chemicals combined.
– specific name i.e. Cotton, linen, silk, wool, silver, rayon, polyester, nylon, acetate, acrylic, glass, etc.
Ways of identification of fibres:
-visual inspection – microscopic examination
– burning test –-
-absorbency test,
_ microscopic test
_ feeling test
characteristics of cellulosic fibres:
– they are very absorbent so they dye very well and are able to absorb sweat very well to make them cool and comfortable to use in hot or warm weathers.
– they have low resiliency and therefore wrinkle or crease badly.
– they are non-thermoplastic therefore they can withstand high temperatures without melting, etc.
Properties of protein fibres:
– high resiliency so hang out well and does not crease easily.
– weaker when wet so they relax or shrink if not well washed.
-They are however very strong in their dry state, etc. Wool is a non-conductor of heat: – warm to wear.
– very absorbent and is comfortable to wear in cold weather.
– scaly therefore felts and can irritate the skin in hot or dry weather
– feels dry on the surface in its wet state therefore prevents chill.
Clothing & Textiles /simplified notes for WASSCE
synthetic fibres:
– are thermoplastic therefore melt on exposure to high temperature
– low absorbency so absorbs very little moisture
– high resiliency so they do not wrinkle badly regenerated cellulosic e.g. Rayon, acetate.
natural mineral fibres:
– high density eg. Steel, asbestos, aluminium, gold, glass.
– heavy in weight.
– flame proof so do not burn .
Methods of fabric production:. – weaving
– knitting
– quilting
– crocheting
– lacing
– bonding
– netting
fabric finishes: a finish is treatment given to a fibre, yarn or fabric either before or after constructing the fabric to improve the appearance, hand (feel) and performance.
Types of finishes:
_beetling is a mechanical finish applied to cotton and linen to flatten the yarns to increase luster or sheen.
_calendaring – applied to all fabrics to smoothen their surfaces.
_Mercerization – a chemical finish applied to cellulose fibres. Add luster, improves absorbency,
other methods are:
-Singeing, Sizing, Weighting, bleaching, embossed surfaces, napping, flocking, waterproof, Water repellent, moth proof, Pre-shrunk, Flame proof scotch.
fabric is any material produced from fabrics
Cotton fabrics: Grey baft, Calico/poplin, Wax prints (dumas), plaid, Lawn, muslin, Lace, jersey, Seer- sucker, crinkle, gingham, cotton, Toweling, drill, Corduroy, Cotton velvet, Damask, Denim, Brushed cotton, Flannelette, winceyette, etc.
linen fabrics: damask, Embroidery linen, Suiting linen, Handkerchief linen, lace, gingham, printed linen, Dress linen, sheeting, canvas.
silk fabrics: taffeta, Chiffon, Organza, Washed silk, Silk satin etc.
Woollen fabrics: Tweed, Jersey, Mohair, flannel, Worsted, Gabardine, Cashmere etc.
synthetic fabrics: Acrylic-pile, jersey, Fur, fleece, . Polyamide/nylon, organza, Chiffon, Satin, brocade, Jersey, polyester- Crimplene, Terylene, Dacron, Net, Lace,
Clothing & Textiles /simplified notes for WASSCE
reasons for combinations of fibers: to improve;
– performance,
-care
– aesthetic properties.
blends: different fibres are spun to make yarns to produce a fabric.
mixtures: yarns of different fibres are used to produce the fabric.
Uses of cotton fabrics : –
underwear
– outerwear,
– accessories, etc. – household linen – industrial materials
Usee of linen fabrics :
– outerwear
– accessories
– household linen,
– industrial materials, silk fabrics uses:
– outer garments
– accessories
– outwear
– accessories
– household articles
Nylon fabrics uses:
– undergarments
– outer garments
-accessories
Classification of sewing tools and equipment
-classification of sewing equipment and tools by their functions.
-Classification of sewing equipment and tools based on size: small equipment e.g. Scissors, needle, thimble large equipment e.g. Table, mirror
classification of tools and equipment by function/use:
– pressing tools and equipment eg-iron-ironing board, blanket/pressing cloth-sleeve board-tailors ham
-stitching/sewing tools and equipment eg-bodkin-thimble-pin cushion-pins- hand needle-sewing machine
-fitting tools and equipment eg.-dummy/dress stand-long mirror
-measuring tools and equipment eg-French curve, rule, tape measure, yardstick, T-square-hem gauge
-cutting tools and equipment eg-shears/cutting out scissors
-awl/stiletto
-seam ripper
-pinking shears
-trimming scissors
-paper cutting scissors
-storing tools and equipment-hangers-wardrobe
-jewellery box
-cabinet
-Suit case
Trunk
-marking tools and equipment-tailors chalk-tracing wheel-eraser-pencil-dressmakers carbon
factors that affect the choice of sewing equipment and tools.
– available money
– expertise
-ease to care for
-durability
– space, etc
Clothing & Textiles /simplified notes for WASSCE
Factors to consider in buying the sewing machine
-durability
-money available
-type or brand
-Ability to use
-the purpose of the machine
-availability of space
-availability of spare parts
Ways of caring for the sewing machine -Oil it regularly
-Never use it while any part is loose
-Cover it with its cover when not in use
-remove all pins and threads when the sewing machine is not in use
-servicing it occasionally
Common faults to encounter when using the sewing machine
-missed stitches
–thread breaking
-broken needle
-loops on the wrong side of stitching
-loops on the right side of stitching
. Types of sewing machines:
– hand sewing machine
– treadle sewing machine
– electric sewing machine
Advantages of hand sewing machine
–it is good for beginners-it is portable
-it is less expensive
-Does not occupy much space
-can be used where there is no electricity
Disadvantages of hand sewing Machine
-it works slowly
-it is less efficient
– cannot perform many functions/operations
-only one hand controls the stitching
Advantages of treadle machine
–works faster than hand machine
-does not require the use of electricity
-it is efficient than hand machine
-both hands are free to control the stitching
Disadvantages of treadle machine
-it is expensive than hand machine
-it is slower as compared to electric sewing machine
-it is no good for beginners
-it occupies large space
-it is not portable
-cannot perform many functions
Advantages of electric sewing machine
–it works faster
-both hands are free to control the work-it is efficient
-it saves time and energy
-can perform many operations
Disadvantages of electric sewing machine
-not good for beginners
-cannot be used when there is no light
-it is very expensive
-can develop electric fault
-some are not portable.
Clothing & Textiles /simplified notes for WASSCE
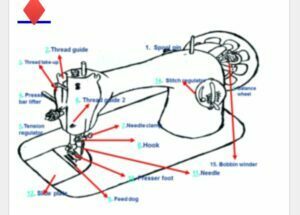
Parts of the sewing machine and their functions:
– handle -use to set the machine into motion
– balanced wheel-controls the movement of the sewing machine
– feed dog, – pushes fabric forwards and backwards when sewing
-presser foot- holds fabric in position when sewing
-spool pin- it holds the reel of the thread
-bobbin- thread is wind on it
-stitch regulator-regulates the length of stitches
-bobbin winder-for winding thread around the bobbin
– thread guide-holds the thread in position
-tension disc- regulates the tension of the thread (tightening and losing the
-thread)-thread-take-up leaver-controls the flow of the thread in the needle
classification of stitches:
1. Temporary stitches. They are stitches that are removed after serving their purpose eg.
– long and short tacking
– even tacking
– diagonal tacking
– tailors tacking, etc.
2. permanent stitches-they are stitches that remain in the garment for long time.
Types of permanent stitches
– joining stitches e.g. Back, running
– neatening stitches e.g. Blanket hemming
– decorative stitches, e.g. Sating, herringbone [stitches for holding finished edges]
General rules for working stitches
– thread must be suitable in texture and colour
– use correct needle type/size for stitches being made
– fasten on and off securely, etc.
Seams:
Means joining two or more layers of fabrics together neatly and securely with a permanent stitch.
Groups of seams:
– conspicuous seams e.g. Overlaid seam – -inconspicuous seam e.g. French seam
factors affecting choice of seams:
– the wearer
– style
– position, Etc.
General rules for making seams:
-thread for making seams must be suitable to that fabric
– width of seam should suit the texture of fabric.
Examples of seams:
– french.
– plain (open or closed).
– overlaid
– top stitched
– machine fell all seams
methods of arranging fullness: – it is the process of doing away with axcess part of a garments eg.
-gathering
– smocking
– darts, etc.
factors to consider in choosing:
– fabric
– figure type
– purpose for which articles will be used, etc preparing
Check on
https://educationalhealthynews.com/opinions/bdt_bece-2021how-economics/
Methods of arranging different fullness:
– darts
– pleats
– gathers
– shirring Edge finishes:
– processes worked on raw edges of articles.
reasons for finishing edges:
– to prevent fraying
– to neaten
– to strengthen
– to decorate
– for style, etc.
edges that require finishing:
-necklines,
-armholes
, -hems
,- table cloths,
-chair backs, etc.
Types of edge finishes:
– facing
– binding
– hems
– single layer and double layer finishing
– attaching lace
Points to consider when choosing edge finishes:
– fabric being used.
– the type of article
– position of the edge, etc. Finishing edges by
– facing
– binding
– hemming
– attaching lace
Openings: They are spaces found on garments that help to put on and take off the garments easily.
Types/examples openings
-continuous wrap
, -bound opening
-box-pleat
,-hem opening
-Placket opening
-fly front opening
-slit opening-zipper opening
-faced slit opening
Clothing & Textiles /simplified notes for WASSCE
classification of openings:
– overlapping
– openings with meeting edges.
factors that influence the selection of openings:
– position on the article
– age of wearer
– style of article
-type of fasteners to use
Importance of openings
-serves as a design feature
-for decoration
-for easy wearing of garments
-for easy taking off of garments
-as a style feature
fastenings: they are devices use to close openings.
Points to consider in choosing fastenings:
– type of opening
– age of wearer
-type of garment
– style of article, etc.
Examples of fastenings:
– press studs
-velcro-eyelet and holes
– hook and eye
-hook and bar-zipper
– buttons and button
-holes
– zipper
Importance of fasteners
–for decoration
-as a style feature
-to close openings
-for identification
-it gives shape to the garment
-allows garment to be constructed in a close
-fitting style
Pockets. They are shapes found on garments used for storing or keeping objects
Importance of pockets
–as a style feature
-for decoration
-for keeping items (for functional)
-for identification
-to hide flaws on garments types of pockets:- patch pocket, -bound pocket, -welt pocket,
Source
Read also on